As a firm evaluates all of its projects takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. The evaluation of projects is a critical component of any organization’s decision-making process, and it is essential for ensuring that resources are allocated to the projects that will generate the greatest value.
This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the project evaluation process, including the key factors to consider, the different evaluation techniques available, and the importance of risk assessment and sensitivity analysis. By following the guidance provided in this guide, firms can improve the quality of their project evaluations and make better investment decisions.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Project Evaluation Criteria
Project evaluation is a systematic process that assesses the viability and desirability of a proposed project. It involves identifying and analyzing relevant factors to determine whether the project should be undertaken.
Key factors considered in project evaluation include:
- Financial feasibility: This involves assessing the project’s financial viability, including its costs, revenues, and profitability.
- Technical feasibility: This assesses the project’s technical viability, including its technological requirements, resource availability, and potential risks.
- Market feasibility: This assesses the project’s market potential, including the size and characteristics of the target market, competitive landscape, and potential demand.
- Operational feasibility: This assesses the project’s operational feasibility, including its organizational structure, resource allocation, and operational procedures.
Industry-Standard Methods for Assessing Project Feasibility
Industry-standard methods for assessing project feasibility include:
- Cost-benefit analysis: This method compares the project’s costs and benefits to determine its overall economic viability.
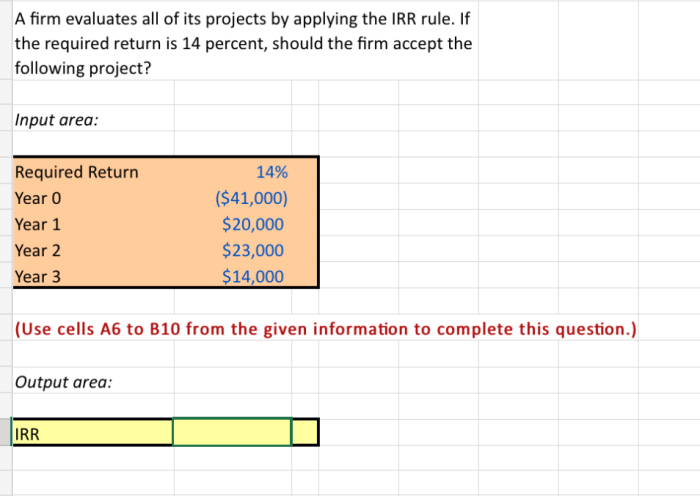
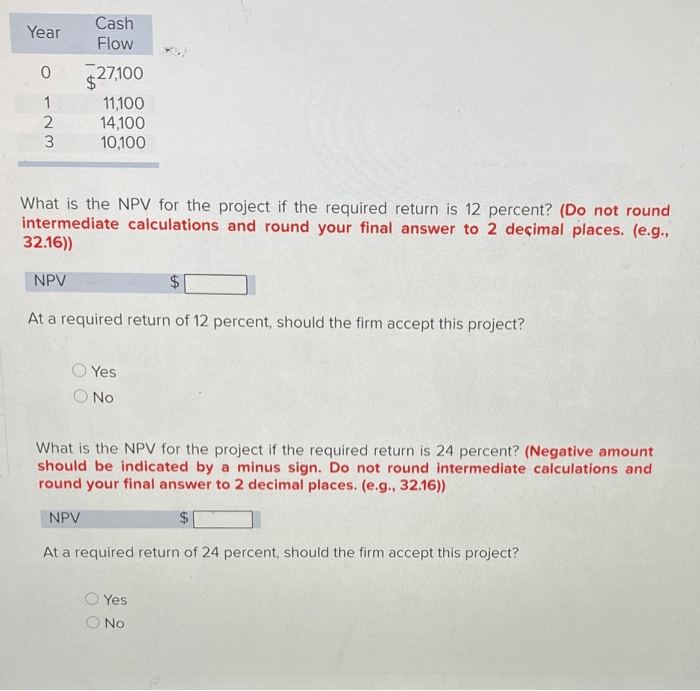
- Net present value (NPV): This method calculates the present value of the project’s future cash flows to determine its profitability.
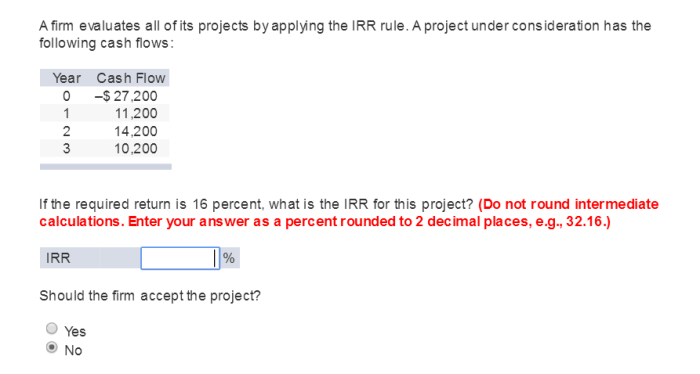
- Internal rate of return (IRR): This method calculates the discount rate that makes the project’s NPV equal to zero, indicating the project’s profitability.
- Payback period: This method calculates the time it takes for the project to generate enough cash flow to cover its initial investment.
Financial and Non-Financial Metrics Used in Project Evaluations
Financial metrics used in project evaluations include:
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Profitability index
- Cash flow
- Net income
Non-financial metrics used in project evaluations include:
- Customer satisfaction
- Employee morale
- Environmental impact
- Social impact
Evaluation Process: A Firm Evaluates All Of Its Projects

Project evaluation is a systematic process of assessing the viability and potential benefits of a project. It involves various steps, from project identification to monitoring and evaluation.
The evaluation process is crucial for making informed decisions about project selection, resource allocation, and risk management.
Role of Stakeholders
Stakeholders play a significant role in project evaluation. They provide valuable input and insights based on their knowledge, interests, and perspectives.
- Project Sponsors:Define the project’s goals and objectives.
- Project Team:Provides technical expertise and estimates project costs and timelines.
- End-Users:Identify their needs and expectations for the project.
- External Stakeholders:May include regulators, community members, or investors.
Best Practices for Objectivity and Transparency
To ensure objectivity and transparency in project evaluations, several best practices should be followed:
- Establish Clear Evaluation Criteria:Define specific metrics and benchmarks to assess project performance.
- Involve Independent Evaluators:Engage external experts to provide unbiased assessments.
- Document the Evaluation Process:Keep detailed records of all evaluation activities, including assumptions and data sources.
- Communicate Evaluation Results:Share the evaluation findings with stakeholders in a clear and concise manner.
Evaluation Techniques
Project evaluation techniques are used to assess the financial viability and potential return on investment of a project. These techniques consider factors such as initial investment, cash flows, and time value of money to determine the project’s profitability and risk.
There are several commonly used project evaluation techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
Net Present Value (NPV)
- Advantages:NPV considers the time value of money and provides a comprehensive measure of a project’s profitability.
- Disadvantages:NPV can be sensitive to changes in discount rate and may not accurately reflect the project’s risk.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Advantages:IRR provides a single metric that represents the project’s profitability and is not affected by the choice of discount rate.
- Disadvantages:IRR can be difficult to calculate and may not always be unique, especially for projects with complex cash flows.
Payback Period
- Advantages:Payback period is easy to calculate and provides a quick assessment of a project’s liquidity.
- Disadvantages:Payback period does not consider the time value of money and may not accurately reflect the project’s profitability.
The choice of project evaluation technique depends on the specific project and the decision-maker’s preferences. In practice, multiple techniques are often used in combination to provide a more comprehensive evaluation.
For example, a company considering a new product launch may use NPV to assess the project’s profitability, IRR to compare it to other investment opportunities, and payback period to evaluate its liquidity. By combining these techniques, the company can make a more informed decision about whether to proceed with the project.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is a critical component of project evaluation as it helps identify and mitigate potential risks that may impact project success. It involves evaluating the probability and severity of risks and developing strategies to minimize their impact.
There are various methods for identifying and evaluating project risks, including qualitative and quantitative techniques. Qualitative methods involve using expert judgment and experience to assess risks, while quantitative methods use numerical data and statistical analysis to estimate risk probabilities and impacts.
Methods for Identifying and Evaluating Risks, A firm evaluates all of its projects
- Brainstorming:Involves gathering a group of experts to identify potential risks based on their knowledge and experience.
- Interviews:Conducting interviews with project stakeholders, including team members, clients, and subject matter experts, to gather their perspectives on potential risks.
- Historical data analysis:Reviewing past project data to identify common risks and their impact on project outcomes.
- Risk matrices:Using a matrix to evaluate the probability and impact of risks, assigning numerical values to each risk factor.
- Monte Carlo simulation:A quantitative technique that uses random sampling to simulate possible project outcomes and estimate the probability of risks occurring.
Once risks are identified and evaluated, project managers can develop strategies to mitigate their impact. This may involve avoiding risks altogether, transferring risks to third parties, or developing contingency plans to respond to risks if they occur.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Risk avoidance:Identifying and eliminating potential risks by changing project plans or selecting alternative approaches.
- Risk transfer:Transferring the responsibility for managing risks to third parties, such as insurance companies or subcontractors.
- Risk mitigation:Developing strategies to reduce the probability or impact of risks, such as implementing additional controls or contingency plans.
Effective risk assessment and mitigation are essential for enhancing project success. By proactively identifying and managing risks, project managers can increase the likelihood of achieving project objectives and minimize the impact of potential setbacks.
Sensitivity Analysis

Sensitivity analysis is a valuable tool in project evaluation, allowing project managers to assess the impact of changing project variables on project outcomes. It helps identify the most critical project assumptions and potential risks, enabling informed decision-making.
Techniques for Conducting Sensitivity Analysis
Two common techniques for conducting sensitivity analysis are:
- Scenario analysis:Involves evaluating the project under different sets of assumptions, representing potential scenarios.
- Monte Carlo simulation:Uses random sampling to generate multiple project outcomes, providing a probabilistic distribution of potential outcomes.
By varying project variables and observing the corresponding changes in project outcomes, sensitivity analysis provides insights into the project’s robustness and potential vulnerabilities.
Decision-Making
Project evaluation decisions are critical to the success of any organization. Several factors must be considered when making these decisions, including both quantitative and qualitative factors. It is important to weigh the pros and cons of each project carefully before making a decision.
Quantitative factors are those that can be measured and quantified, such as the project’s cost, benefits, and risks. Qualitative factors are those that cannot be easily measured, such as the project’s impact on the environment or the community. Both quantitative and qualitative factors should be considered when making project evaluation decisions.
Importance of Considering Both Quantitative and Qualitative Factors
Quantitative factors are important because they provide a way to compare different projects on an objective basis. Qualitative factors are important because they can provide insights into the project’s potential impact that may not be captured by quantitative factors. By considering both quantitative and qualitative factors, decision-makers can make more informed decisions about which projects to approve.
Presenting Project Evaluation Findings and Recommendations to Stakeholders
Once the project evaluation has been completed, the findings and recommendations should be presented to stakeholders. This can be done in a variety of ways, such as a written report, a presentation, or a meeting. It is important to present the findings in a clear and concise manner, and to highlight the key points that are most relevant to the stakeholders.
Case Studies
Case studies offer valuable insights into the practical application of project evaluation techniques and the outcomes they produce. By examining both successful and unsuccessful project evaluations, we can identify best practices and lessons learned to enhance future project evaluations.
Successful project evaluations provide a roadmap for effective project planning and execution. They demonstrate the alignment between project objectives and organizational goals, leading to positive outcomes and stakeholder satisfaction. Conversely, unsuccessful project evaluations highlight potential pitfalls and areas for improvement.
They reveal weaknesses in project planning, implementation, or evaluation methods, offering valuable lessons to avoid similar mistakes in the future.
Lessons Learned from Case Studies
- The importance of stakeholder involvement throughout the evaluation process ensures alignment with project objectives and stakeholder expectations.
- Using a structured and standardized evaluation framework enables consistent and objective project assessments.
- Incorporating both qualitative and quantitative data provides a comprehensive understanding of project outcomes and impacts.
- Conducting regular project monitoring and evaluation allows for timely course corrections and adjustments to improve project outcomes.
- Documenting project evaluation processes and findings facilitates knowledge sharing and continuous improvement.
Best Practices in Project Evaluation
- Establish clear and measurable project objectives to guide the evaluation process.
- Involve stakeholders early on to ensure their perspectives and interests are considered.
- Use a combination of evaluation methods to gather both qualitative and quantitative data.
- Conduct regular project monitoring and evaluation to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
- Document project evaluation processes and findings to inform future project planning and evaluation.
Questions and Answers
What are the key factors to consider when evaluating a project?
The key factors to consider when evaluating a project include the project’s financial viability, its strategic alignment with the firm’s objectives, its operational feasibility, and its environmental and social impact.
What are the different evaluation techniques available?
The different evaluation techniques available include Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Payback Period, and Sensitivity Analysis.
What is the importance of risk assessment and sensitivity analysis?
Risk assessment and sensitivity analysis are important because they help firms to identify and mitigate potential risks and uncertainties associated with a project.