Introducing Chapter 4 Section 1 Population Dynamics Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that delves into the intricate mechanisms that govern population dynamics. This resource provides a thorough understanding of the concepts, principles, and factors that influence population growth, density, distribution, and regulation.
Through engaging explanations, real-world examples, and thought-provoking discussions, this answer key unravels the complexities of population dynamics, empowering readers to grasp the fundamental principles that shape the natural world.
1. Population Dynamics
Concepts and Principles

Population dynamics encompasses the study of population growth, density, distribution, and the factors that influence these characteristics. It provides a framework for understanding how populations change over time and space, and how these changes impact ecological systems.
Population growth is influenced by birth rates, death rates, and migration. Density refers to the number of individuals per unit area or volume, while distribution describes the spatial arrangement of individuals within a population. These factors interact to determine population dynamics and shape ecological communities.
Factors Influencing Population Growth
- Birth rates: The number of new individuals added to a population per unit time.
- Death rates: The number of individuals removed from a population per unit time.
- Migration: The movement of individuals into or out of a population.
Examples of Population Dynamics, Chapter 4 section 1 population dynamics answer key
- Population growth in response to increased resource availability.
- Population decline due to disease or predation.
- Population distribution influenced by habitat fragmentation.
2. Population Growth Models: Chapter 4 Section 1 Population Dynamics Answer Key
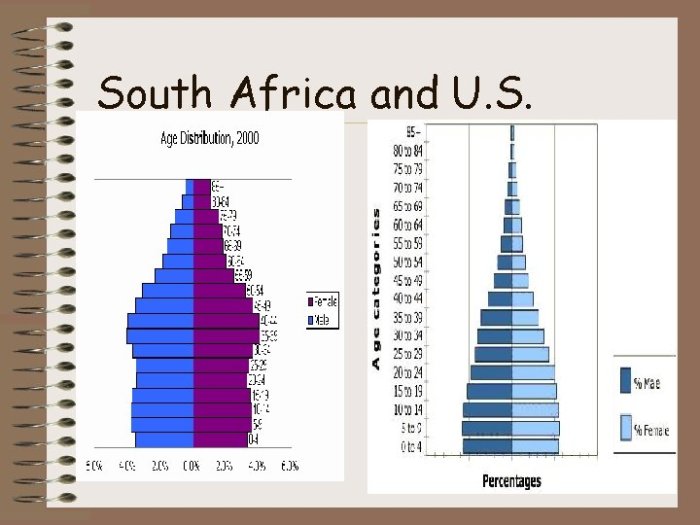
Population growth models are mathematical equations that describe how populations change over time. They provide insights into the dynamics of population growth and can be used to predict future trends.
Types of Population Growth Models
- Exponential growth: Assumes unlimited resources and a constant growth rate.
- Logistic growth: Considers resource limitations and predicts a population that reaches a carrying capacity.
Assumptions and Limitations of Population Growth Models
- Exponential growth: Assumes constant environmental conditions and no resource limitations.
- Logistic growth: Assumes a fixed carrying capacity and symmetrical growth around the carrying capacity.
Examples of Population Growth Models
- Exponential growth model to predict population growth in the absence of limiting factors.
- Logistic growth model to predict population growth in a limited environment.
3. Population Regulation

Population regulation refers to the mechanisms that control population growth and maintain population stability. These mechanisms can be density-dependent or density-independent.
Density-Dependent Factors
- Competition for resources: Limited resources, such as food, water, and shelter, can limit population growth.
- Predation: Predators can reduce population size by consuming individuals.
- Disease: Pathogens and parasites can spread within populations and cause mortality.
Density-Independent Factors
- Environmental disasters: Natural events, such as hurricanes, floods, and fires, can impact population size regardless of density.
- Climate change: Changes in temperature, precipitation, and other environmental factors can affect population growth.
Examples of Population Regulation
- Population growth limited by competition for food in a closed ecosystem.
- Population decline due to a disease outbreak.
- Population stability maintained by a balance between predation and birth rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is population density?
Population density refers to the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume.
How does migration affect population growth?
Migration can increase or decrease population growth depending on whether individuals are entering or leaving the population.
What is the difference between exponential and logistic growth models?
Exponential growth assumes unlimited resources, while logistic growth considers carrying capacity and environmental limitations.