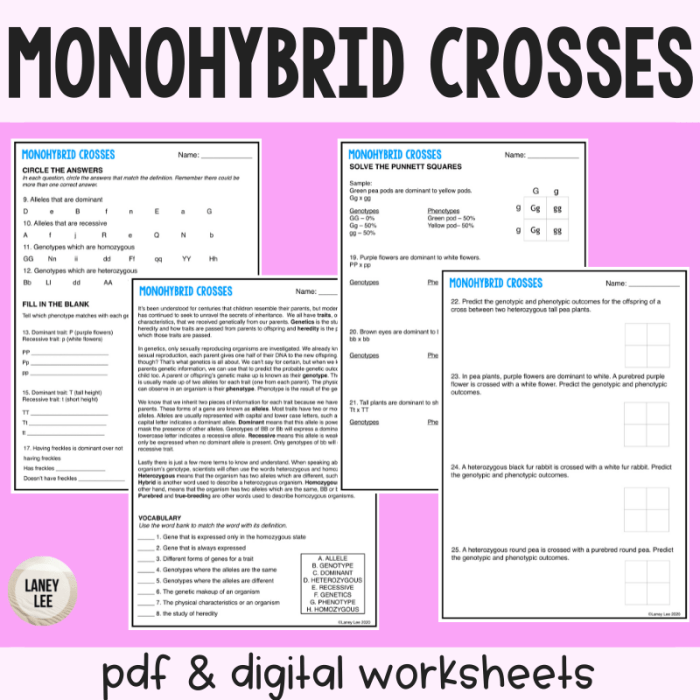
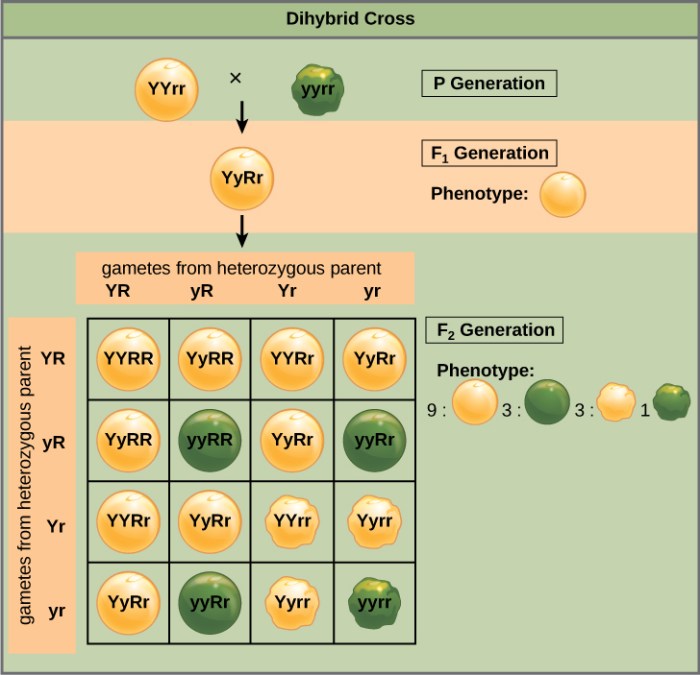
Monohybrid cross practice give peas a chance – Monohybrid cross practice gives peas a chance to reveal the fundamental principles of genetics. This practice, rooted in Gregor Mendel’s pioneering experiments with pea plants, provides a foundation for understanding the inheritance patterns that shape the diversity of life.
Through controlled crosses and meticulous observations, monohybrid cross practice allows researchers to investigate the behavior of single genes and their impact on observable traits. By giving peas a chance to demonstrate the power of genetic principles, this practice illuminates the mechanisms that govern the transmission of heritable characteristics.
Materials and Methods: Monohybrid Cross Practice Give Peas A Chance

To conduct a monohybrid cross experiment using pea plants, the following materials are required:
- Pea plants with contrasting traits (e.g., tall vs. short)
- Tweezers or forceps
- Magnifying glass (optional)
- Notebook or data recording sheet
The step-by-step procedures for performing the cross are as follows:
- Select two pea plants with contrasting traits for the desired characteristic (e.g., tall vs. short).
- Remove the petals from the flowers of one plant (the male parent) to prevent self-pollination.
- Use tweezers or forceps to transfer pollen from the male parent to the stigma of the female parent (the plant with the contrasting trait).
- Cover the pollinated flower to prevent contamination from other pollen sources.
- Allow the pea pods to develop and mature.
- Collect the seeds from the pea pods and plant them to observe the phenotypes of the offspring.
FAQ Compilation
What is the significance of monohybrid crosses in genetics?
Monohybrid crosses are fundamental in genetics as they allow researchers to study the inheritance of a single gene and its impact on a specific trait. This practice provides insights into the principles of dominant and recessive alleles, the laws of segregation and independent assortment, and the genetic basis of phenotypic variation.
How did Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants contribute to the development of monohybrid cross practice?
Gregor Mendel’s meticulous experiments with pea plants laid the foundation for monohybrid cross practice. By carefully controlling the pollination process and observing the inheritance patterns of different traits, Mendel established the fundamental principles of genetics. His work with pea plants provided a model system for studying the behavior of single genes and their role in determining phenotypic characteristics.
What are the applications of monohybrid cross practice in modern genetics?
Monohybrid cross practice remains a valuable tool in modern genetics, contributing to advancements in various fields. It is used in genetic counseling to predict the inheritance of specific traits and identify genetic disorders. In agriculture, monohybrid crosses are employed to develop improved crop varieties with desirable traits, such as increased yield or resistance to pests.
Additionally, this practice finds applications in evolutionary studies, population genetics, and the understanding of genetic diversity.